When it comes to modern surface materials, HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) boards stand out as one of the most versatile, durable, and visually appealing options in the construction and interior design industries. Whether used in public restrooms, kitchen cabinetry, or laboratory countertops, HPL boards combine aesthetic design with high-performance durability—making them a preferred choice among architects, designers, and builders alike.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about HPL boards—from their composition and manufacturing process to their key advantages, types, applications, and the differences between phenolic and urea-formaldehyde resin adhesives.
1. What Is an HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) Board?
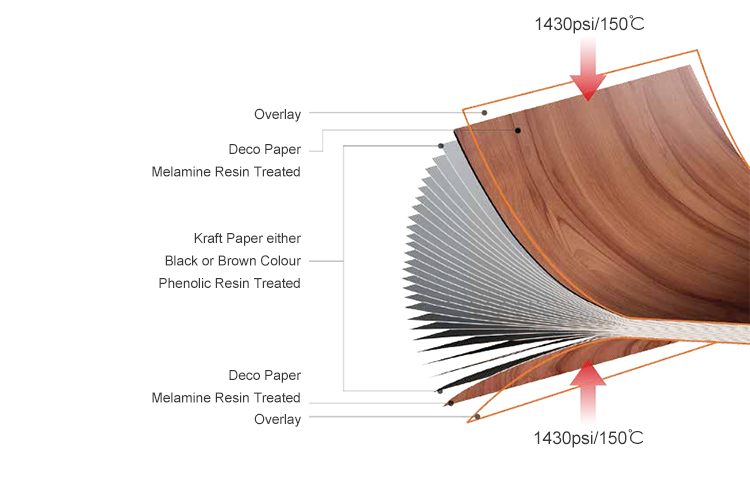
An HPL board, also known as Compact Laminate or HPL Compact Board, is a highly durable decorative surface material made by layering sheets of paper impregnated with thermosetting resins and pressing them under high temperature and pressure.
The process involves:
Decorative colored paper impregnated with melamine resin for surface aesthetics.
Multiple layers of kraft paper impregnated with phenolic resin for structural strength.
Compression under approximately 150°C and 1430 psi of pressure using a textured steel plate.
The thickness of the HPL board can vary (typically 1.6mm to 25mm) depending on the number of kraft paper layers used.
The result is a structurally stable, dense, non-porous, and eco-friendly decorative material suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.

2. The Rise of Second-Generation (Counterfeit) HPL Boards
In recent years, a second-generation HPL board, also referred to as fiberboard or fake HPL, has entered the market. At first glance, it looks almost identical to genuine HPL, but there are critical differences that significantly affect performance.
This imitation version is made of melamine paper combined with wood fibers, resulting in:
While these boards are cheaper, they lack the superior durability, moisture resistance, and longevity of true phenolic-based HPL boards. Therefore, understanding the differences between authentic and counterfeit materials is crucial when selecting HPL products for professional or large-scale applications.
3. How Are HPL Boards Manufactured?
The HPL production process is a complex, multi-step procedure that ensures both the appearance and performance of the finished material meet industry standards.
Here’s how it’s made:
Impregnation – Decorative and kraft papers are individually impregnated with melamine and phenolic resins.
Drying – The sheets are partially dried to remove excess moisture and prepare them for pressing.
Stacking – Multiple sheets are stacked with the decorative surface paper on top.
Pressing – The stack is pressed at high pressure (around 1430 psi) and high temperature (approximately 150°C) using steel plates to imprint textures and bind the layers.
Cooling and Trimming – The compacted sheet is cooled, trimmed, and sanded to achieve uniform dimensions and surface smoothness.
This heat and pressure fusion process gives HPL boards their unique combination of hardness, stability, and aesthetic versatility.
4. Superior Performance of HPL Boards
The remarkable properties of HPL boards make them suitable for demanding environments. Let’s explore their key advantages:
1. Wear and Scratch Resistance
HPL’s dense surface structure makes it highly resistant to scratches, abrasion, and impact, maintaining its finish even under heavy use.
2. Waterproof and Moisture-Proof
The non-porous surface and phenolic core prevent water penetration, ensuring excellent moisture resistance—a vital quality in restrooms, kitchens, and outdoor furniture.
3. Fire and Heat Resistance
HPL is fire-retardant and heat-resistant, providing safety in commercial kitchens, laboratories, and public facilities.
4. Chemical Resistance
The surface resists damage from acids, bases, and cleaning agents, making it suitable for laboratory and healthcare applications.
5. Hygienic and Antibacterial
HPL’s smooth, non-porous finish resists mold and bacterial growth, ensuring hygiene in hospitals, schools, and bathrooms.
6. Eco-Friendly and Safe
High-quality phenolic resin-based HPL boards emit minimal formaldehyde, meeting strict environmental standards and ensuring user safety.
7. Stable and Non-Deforming
Even under temperature or humidity fluctuations, HPL maintains its shape and dimensional stability.
8. Design Versatility
Available in various textures, finishes, and colors, HPL offers creative freedom for designers and architects.
5. Applications of HPL Boards
Thanks to their durability, safety, and design flexibility, HPL boards are used across a wide range of industries and environments.
Common HPL Board Applications Include:
Public Restroom Partitions and Toilet Cubicles
Bathroom Vanities and Countertops
Storage Cabinets and Kitchen Cabinets
Interior Doors and Wall Cladding
Laboratory Worktops and Benches
School Desks and Lockers
Office Furniture and Meeting Tables
Outdoor Benches and Façade Panels
In both commercial and residential settings, HPL boards provide a balance of functionality and aesthetics, ideal for high-traffic, high-performance areas.
6. Classification of HPL Boards
HPL boards can be categorized based on their applications and performance requirements into three main types:
1. Indoor HPL Boards
These are the most common and versatile types, featuring wear resistance, fire retardancy, antibacterial, and antistatic properties.
Applications:
Airport counters
Public restrooms
Station windbreaks
School furniture
Canteen tables
Wardrobes
2. Outdoor HPL Boards
Designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, outdoor HPL boards come in solid, natural, and metallic color series.
They are UV-resistant, weatherproof, and fade-resistant.
Applications:
Building façades
Balcony panels
Outdoor furniture
Public installations
3. Laboratory HPL Boards (Chemical-Resistant Boards)
Specially engineered for chemical and biological laboratories, these boards have enhanced resistance to solvents, acids, and bases.
Applications:
Science labs
Research centers
Medical testing areas
Industrial workstations
7. Understanding Resin Adhesives in HPL Boards
A crucial factor determining the quality and safety of HPL boards lies in the type of resin adhesive used.
There are two main types of resin adhesives in HPL production:
Phenolic Resin
Urea-Formaldehyde Resin
Let’s examine how these affect the final product.
8. Phenolic Resin vs. Urea-Formaldehyde Resin: What’s the Difference?
Phenolic Resin HPL Boards
High bonding strength: Ensures tight adhesion between layers, minimizing delamination or bubbling.
Superior durability: Excellent fire resistance, moisture resistance, and chemical stability.
Environmental safety: Although phenolic resin contains formaldehyde, the amount of free formaldehyde released is very low, making it more eco-friendly.
Stable performance: Less prone to deformation or deterioration over time.
Urea-Formaldehyde Resin HPL Boards
Lower cost: Manufacturers use this resin to reduce expenses.
Inferior performance: Poorer bonding strength, water resistance, and heat resistance.
Higher formaldehyde emission: Not ideal for applications where indoor air quality or safety is critical.
Conclusion:
If longevity, safety, and performance matter, phenolic resin HPL boards are the superior choice despite their slightly higher cost.
9. How to Identify Genuine HPL Boards
Because counterfeit HPL boards look similar to authentic ones, it’s essential to know how to distinguish between them.
Here are some tips:
Weight and Density: Genuine HPL feels denser and heavier.
Surface Quality: Authentic boards have consistent texture and color with a harder feel.
Water Test: Immerse a sample in water for 24 hours—fake boards will swell or delaminate.
Brand Verification: Always purchase from reputable manufacturers or certified distributors.
10. Why Choose HPL Boards for Modern Design
HPL boards embody the perfect combination of functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability. They are suitable for:
Architectural exteriors needing long-term weather durability.
Commercial interiors requiring easy maintenance and hygiene.
Educational and medical environments that demand chemical and bacterial resistance.
Custom furniture that blends modern design with robust performance.
Their long service life, color stability, and customization options make HPL a go-to material in modern construction and interior projects.
11. Key Factors to Consider When Buying HPL Boards
Before purchasing HPL boards, consider the following:
Intended Application (Indoor, Outdoor, or Laboratory)
Thickness and Size Requirements
Surface Finish and Color Options
Fire and Chemical Resistance Ratings
Formaldehyde Emission Levels (E1 or E0 Grade)
Manufacturer Reputation and Certification (ISO, SGS, GREENGUARD)
By paying attention to these details, you can ensure that your investment delivers maximum value, safety, and longevity.
12. Conclusion
In conclusion, HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) boards have revolutionized the design and construction industries with their exceptional performance, versatility, and eco-friendly properties. Whether used for bathroom partitions, kitchen cabinets, laboratory tables, or building façades, HPL offers long-lasting beauty, safety, and reliability.
While cheaper imitations such as fiberboard HPL may seem attractive, they cannot match the strength, moisture resistance, and fire safety of genuine phenolic resin HPL boards.
When it comes to quality surfaces that withstand time, temperature, and usage, HPL boards remain the undisputed leader—combining durability, aesthetic excellence, and sustainability in one powerful material.
English
Русский
العربية
Français
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
Bahasa Melayu
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Māori
සිංහල
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Беларуская мова
Bosanski
Български
ქართული
Lietuvių
Malti
Runasimi