The kitchen is the heart of every home, so choosing the right decorative materials for it is a top priority for homeowners during renovations. Among the most popular options for kitchen cabinetry and countertops are thermoformed panels and HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) fireproof boards. While both are widely used in interior design, they differ significantly in composition, manufacturing process, performance, and application scenarios. Let’s break down their key differences with Polybett to help you make an informed choice.

First, Let’s Clarify: What Are HPL Fireproof Boards?
HPL fireproof boards (also known as high-pressure laminate fire-retardant boards) are composite materials engineered for durability and safety. Their core structure consists of three key layers:
Kraft Paper Layers: Multiple layers of high-density kraft paper form the base, which determines the board’s structural strength and thickness. The more layers of kraft paper used, the higher the board’s impact resistance and load-bearing capacity.
Colored Paper Layer: A middle layer of colored paper that defines the board’s base color and basic appearance.
Surface Paper Layer: A top layer of specialized surface paper treated with UV-resistant technology. This layer can withstand over a decade of UV exposure without fading and provides excellent heat resistance—critical for kitchen environments where hot cookware is frequently placed.
Manufacturing Process of HPL Fireproof Boards
The production process involves stacking the kraft paper, colored paper, and surface paper layers, then impregnating the entire stack with a melamine resin solution. After impregnation, the stack is pressed under high temperature (120–160℃) and high pressure (1,000–1,400 psi) to form a dense, rigid board. This melamine impregnation step significantly enhances the board’s key properties: wear resistance, scratch resistance, washability, corrosion resistance, and acid resistance.
Note: The "double-sided melamine boards" (also called melamine-faced boards or one-time extruded boards) commonly found in the market follow a similar process but use thinner kraft paper. As a result, they have slightly lower cushioning performance and absorb less melamine resin—leading to reduced wear and scratch resistance compared to premium HPL fireproof boards. However, they excel in flatness, making them a cost-effective alternative for less demanding applications.
Core Characteristics of HPL Fireproof Boards
A standout feature of HPL fireproof boards is their inability to be thermoformed. Due to their rigid, dense structure formed by high-pressure bonding, they cannot be bent or shaped into curved or irregular designs. They are limited to flat surfaces or simple straight-edge applications.
Tip for Selection: Matte-finish HPL fireproof boards are recommended for most residential renovations. Domestic hot-pressing or cold-pressing equipment often has inconsistencies in pressure distribution; flaws or unevenness in the board’s surface are more likely to be visible on glossy finishes, whereas matte finishes can mask minor imperfections.
Second, What Are Thermoformed Panels?
Thermoformed panels (also known as vacuum-formed panels) are decorative boards made by bonding a plastic film to a substrate (typically MDF, particleboard, or eco-board) using vacuum thermoforming technology. They are primarily valued for their ability to create curved, seamless, and custom-designed surfaces—making them a favorite for modern, stylish kitchen cabinetry. Thermoformed panels are generally categorized into three types based on their structure: single-sided thermoformed, double-sided thermoformed, and framed thermoformed panels.
1. Single-Sided Thermoformed Panels
Production Process: A single sheet of plastic film is bonded to one side of an eco-board (or similar substrate) via vacuum thermoforming, while the other side is covered with a thin waterproof paper. This paper provides basic moisture resistance but has almost no tensile strength.
Key Limitations: The main appeal of single-sided thermoforming is the ability to create intricate edge designs (e.g., rounded edges, decorative grooves) by milling the board. However, milling disrupts the board’s internal stress balance. Since the backside paper offers no meaningful tensile support, the panel may remain stable for the first 2–3 years but is prone to issues like warping, film peeling, or edge cracking over time.
Critical Factor: Film Elongation Rate. The plastic film must stretch during the thermoforming process to bond tightly to the milled edges. Domestic plastic films typically have an elongation rate of 11–13 cm (can stretch from 11 cm to 13 cm without tearing), while high-quality German-brand films can stretch up to 18 cm. A higher elongation rate directly reduces the risk of film cracking or deformation at the edges of the board.
2. Double-Sided Thermoformed Panels
Production Process: Unlike single-sided panels, double-sided thermoformed panels have plastic film bonded to both sides of the substrate via a one-step vacuum thermoforming process. The film thickness on both sides is consistent, and the process uses uniform air pressure and temperature—ensuring balanced internal stress across the entire board.
Key Advantages: Even when intricate designs are milled on the front side, the balanced stress from the double-sided film prevents significant warping or deformation. Double-sided thermoformed panels have a longer lifespan, typically lasting 7–9 years (or more) with proper maintenance—making them a more reliable choice than single-sided options.
3. Framed Thermoformed Panels
Structure: This type is a variation of double-sided thermoforming. It consists of four connected side frames (all double-sided thermoformed) joined together using two 50×08 size rods. A central MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) sheet acts as a support core. However, some high-quality versions use particleboard instead of MDF—since particleboard has higher structural strength and lower deformation rates than MDF, further enhancing the panel’s durability.
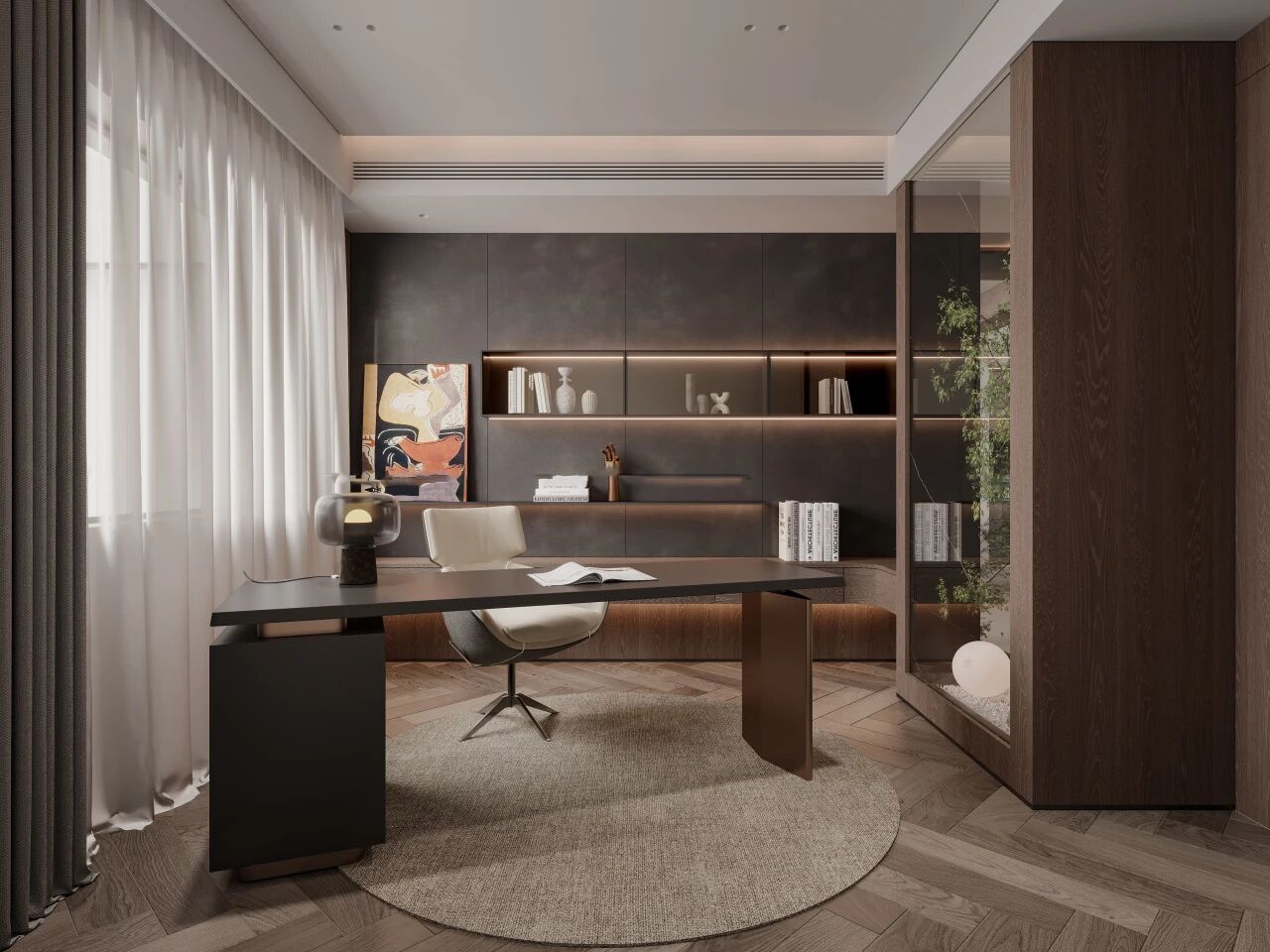

Core Differences Between Thermoformed Panels and HPL Fireproof Boards
| Comparison Dimension | HPL Fireproof Boards | Thermoformed Panels |
| Core Composition | Multiple layers of kraft paper + colored paper + UV-treated surface paper, impregnated with melamine resin. | Substrate (MDF/particleboard/eco-board) + plastic film (single or double-sided) bonded via vacuum thermoforming. |
| Manufacturing Process | High-temperature, high-pressure pressing after melamine impregnation. | Vacuum thermoforming to bond plastic film to substrate; may involve edge milling for custom designs. |
| Formability | Cannot be thermoformed; limited to flat surfaces and straight edges. | Excellent formability; can create curved, seamless, and intricate designs (rounded edges, grooves, etc.). |
| Durability | High wear/scratch resistance, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance; long lifespan (15–30 years for premium options). | Depends on type: Single-sided (2–3 years stable); double-sided/framed (7–9+ years). Film may peel if exposed to excessive heat. |
| Surface Finish | Matte or glossy; matte recommended for hiding minor pressing flaws (domestic equipment). | Smooth, seamless film finish; wide range of colors/patterns available (wood grain, solid colors, etc.). |
| Key Strengths | Fire resistance, high durability, easy maintenance, UV resistance (no fading). | Stylish custom designs, seamless surfaces, curved shapes, modern aesthetic. |
| Key Limitations | No formability; cannot create curved designs. | Single-sided options prone to warping; lower heat resistance than HPL; film may scratch over time. |
| Ideal Applications | Kitchen countertops, high-traffic cabinetry, commercial kitchens (where durability/heat resistance are critical). | Kitchen cabinet doors, wardrobe doors, decorative wall panels (where design/aesthetics are prioritized). |
Final Recommendation
Choosing between thermoformed panels and HPL fireproof boards ultimately depends on your priorities: If you value durability, heat resistance, and low maintenance (e.g., for kitchen countertops or high-use cabinetry), HPL fireproof boards are the better choice. If you prioritize stylish, seamless designs with curved or custom shapes (e.g., for cabinet doors or accent walls), opt for double-sided or framed thermoformed panels (avoid single-sided options for long-term use).
By understanding these core differences, you can select the material that best fits your kitchen’s functional needs and aesthetic preferences—ensuring a renovation that stands the test of time.
English
Русский
العربية
Français
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
Bahasa Melayu
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Māori
සිංහල
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Беларуская мова
Bosanski
Български
ქართული
Lietuvių
Malti
Runasimi